Tennessee is a state located in the southeastern United States. Tennessee is the 36th largest and the 17th most populous of the 50 United States. Tennessee is bordered by Kentucky and Virginia to the north, North Carolina to the east, Georgia, Alabama, and Mississippi to the south, and Arkansas and Missouri to the west. The Appalachian Mountains dominate the eastern part of the state, and the Mississippi River forms the state’s western border. Tennessee’s capital and second largest city is Nashville, which has a population of 601,222. Memphis is the state’s largest city, with a population of 653,450.
The state of Tennessee is rooted in the Watauga Association, a 1772 frontier pact generally regarded as the first constitutional government west of the Appalachians. What is now Tennessee was initially part of North Carolina, and later part of the Southwest Territory. Tennessee was admitted to the Union as the 16th state on June 1, 1796. Tennessee was the last state to leave the Union and join the Confederacy at the outbreak of the U.S. Civil War in 1861. Occupied by Union forces from 1862, it was the first state to be readmitted to the Union at the end of the war.
Tennessee furnished more soldiers for the Confederate Army than any other state, and more soldiers for the Union Army than any other Southern state. Beginning during Reconstruction, it had competitive party politics, but a Democratic takeover in the late 1880s resulted in passage of disfranchisement laws that excluded most blacks and many poor whites from voting. This sharply reduced competition in politics in the state until after passage of civil rights legislation in the mid-20th century. In the 20th century, Tennessee transitioned from an agrarian economy to a more diversified economy, aided by massive federal investment in the Tennessee Valley Authority and, in the early 1940s, the city of Oak Ridge. This city was established to house the Manhattan Project’s uranium enrichment facilities, helping to build the world’s first atomic bomb, which was used during World War II.
Tennessee has played a critical role in the development of many forms of American popular music, including rock and roll, blues, country, and rockabilly. Beale Street in Memphis is considered by many to be the birthplace of the blues, with musicians such as W.C. Handy performing in its clubs as early as 1909. Memphis is also home to Sun Records, where musicians such as Elvis Presley, Johnny Cash, Carl Perkins, Jerry Lee Lewis, Roy Orbison, and Charlie Rich began their recording careers, and where rock and roll took shape in the 1950s. The 1927 Victor recording sessions in Bristol generally mark the beginning of the country music genre and the rise of the Grand Ole Opry in the 1930s helped make Nashville the center of the country music recording industry. Three brick-and-mortar museums recognize Tennessee’s role in nurturing various forms of popular music: the Memphis Rock N’ Soul Museum, the Country Music Hall of Fame and Museum in Nashville, and the International Rock-A-Billy Museum in Jackson. Moreover, the Rockabilly Hall of Fame, an online site recognizing the development of rockabilly in which Tennessee played a crucial role, is based in Nashville.
Tennessee’s major industries include agriculture, manufacturing, and tourism. Poultry, soybeans, and cattle are the state’s primary agricultural products, and major manufacturing exports include chemicals, transportation equipment, and electrical equipment. The Great Smoky Mountains National Park, the nation’s most visited national park, is headquartered in the eastern part of the state, and a section of the Appalachian Trail roughly follows the Tennessee-North Carolina border. Other major tourist attractions include the Tennessee Aquarium in Chattanooga; Dollywood in Pigeon Forge; the Parthenon, the Country Music Hall of Fame and Museum, and Ryman Auditorium in Nashville; the Jack Daniel’s Distillery in Lynchburg; and Elvis Presley’s Graceland residence and tomb, the Memphis Zoo, and the National Civil Rights Museum in Memphis.
Tennessee is known as the “Volunteer State”, a nickname some claimed was earned during the War of 1812 because of the prominent role played by volunteer soldiers from Tennessee, especially during the Battle of New Orleans. Other sources differ on the origin of the state nickname; according to the Columbia Encyclopedia, the name refers to volunteers for the Mexican–American War. This explanation is more likely, because President Polk’s call for 2,600 nationwide volunteers at the beginning of the Mexican-American War resulted in 30,000 volunteers from Tennessee alone, largely in response to the death of Davy Crockett and appeals by former Tennessee Governor and now Texas politician, Sam Houston.
Geography
See also: List of counties in Tennessee and Geology of Tennessee

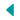
Map of Tennessee
Tennessee borders eight other states: Kentucky and Virginia to the north; North Carolina to the east; Georgia, Alabama, and Mississippi on the south; Arkansas and Missouri on the Mississippi River to the west. Tennessee ties Missouri as the state bordering the most other states. The state is trisected by the Tennessee River.
The highest point in the state is Clingmans Dome at 6,643 feet (2,025 m). Clingmans Dome, which lies on Tennessee’s eastern border, is the highest point on the Appalachian Trail, and is the third highest peak in the United States east of the Mississippi River. The state line between Tennessee and North Carolina crosses the summit. The state’s lowest point is the Mississippi River at the Mississippi state line (the lowest point in Memphis, nearby, is at 195 ft (59 m)). The geographical center of the state is located in Murfreesboro.
The state of Tennessee is geographically, culturally, economically, and legally divided into three Grand Divisions: East Tennessee, Middle Tennessee, and West Tennessee. The state constitution allows no more than two justices of the five-member Tennessee Supreme Court to be from one Grand Division and a similar rule applies to certain commissions and boards.
Tennessee features six principal physiographic regions: the Blue Ridge, the Appalachian Ridge and Valley Region, the Cumberland Plateau, the Highland Rim, the Nashville Basin, and the Gulf Coastal Plain. Tennessee is home to the most caves in the United States, with over 10,000 documented caves to date.
East Tennessee
Main article: East Tennessee

Map of Tennessee highlighting East Tennessee
The Blue Ridge area lies on the eastern edge of Tennessee, bordering North Carolina. This region of Tennessee is characterized by the high mountains and rugged terrain of the western Blue Ridge Mountains, which are subdivided into several subranges, namely the Great Smoky Mountains, the Bald Mountains, the Unicoi Mountains, the Unaka Mountains and Roan Highlands, and the Iron Mountains.
The average elevation of the Blue Ridge area is 5,000 feet (1,500 m) above sea level. Clingmans Dome, the state’s highest point, is located in this region. The Blue Ridge area was never more than sparsely populated, and today much of it is protected by the Cherokee National Forest, the Great Smoky Mountains National Park, and several federal wilderness areas and state parks.
Bald Mountains
Stretching west from the Blue Ridge for approximately 55 miles (89 km) is the Ridge and Valley region, in which numerous tributaries join to form the Tennessee River in the Tennessee Valley. This area of Tennessee is covered by fertile valleys separated by wooded ridges, such as Bays Mountain and Clinch Mountain. The western section of the Tennessee Valley, where the depressions become broader and the ridges become lower, is called the Great Valley. In this valley are numerous towns and two of the region’s three urban areas, Knoxville, the 3rd largest city in the state, and Chattanooga, the 4th largest city in the state. The third urban area, the Tri-Cities, comprising Bristol, Johnson City, and Kingsport and their environs, is located to the northeast of Knoxville.
The Cumberland Plateau rises to the west of the Tennessee Valley; this area is covered with flat-topped mountains separated by sharp valleys. The elevation of the Cumberland Plateau ranges from 1,500 to about 2,000 feet (460 to about 610 m) above sea level.
East Tennessee has several important transportation links with Middle and West Tennessee, as well as the rest of the nation and the world, including several major airports and interstates. Knoxville’s McGhee Tyson Airport (TYS) and Chattanooga’s Chattanooga Metropolitan Airport (CHA), as well as the Tri-Cities’ Tri-Cities Regional Airport (TRI), provide air service to numerous destinations. I-24, I-81, I-40, I-75, and I-26 along with numerous state highways and other important roads, traverse the Grand Division and connect Chattanooga, Knoxville, and the Tri-Cities, along with other cities and towns such as Cleveland, Athens, and Sevierville.
Middle Tennessee
West of the Cumberland Plateau is the Highland Rim, an elevated plain that surrounds the Nashville Basin. The northern section of the Highland Rim, known for its high tobacco production, is sometimes called the Pennyroyal Plateau; it is located primarily in Southwestern Kentucky. The Nashville Basin is characterized by rich, fertile farm country and great diversity of natural wildlife.
Middle Tennessee was a common destination of settlers crossing the Appalachians from Virginia in the late 18th century and early 19th century. An important trading route called the Natchez Trace, created and used for many generations by American Indians, connected Middle Tennessee to the lower Mississippi River town of Natchez. The route of the Natchez Trace was used as the basis for a scenic highway called the Natchez Trace Parkway.
Some of the last remaining large American chestnut trees grow in this region. They are being used to help breed blight-resistant trees.
Middle Tennessee is one of the primary state population and transportation centers along with the heart of state government. Nashville (the capital), Clarksville, and Murfreesboro are its largest cities. Fifty percent of the US population is within 600 miles (970 km) of Nashville. Interstates I-24, I-40, and I-65 service the Division, meeting in Nashville.
West Tennessee
West of the Highland Rim and Nashville Basin is the Gulf Coastal Plain, which includes the Mississippi embayment. The Gulf Coastal Plain is, in terms of area, the predominant land region in Tennessee. It is part of the large geographic land area that begins at the Gulf of Mexico and extends north into southern Illinois. In Tennessee, the Gulf Coastal Plain is divided into three sections that extend from the Tennessee River in the east to the Mississippi River in the west.
The easternmost section, about 10 miles (16 km) in width, consists of hilly land that runs along the western bank of the Tennessee River. To the west of this narrow strip of land is a wide area of rolling hills and streams that stretches all the way to the Mississippi River; this area is called the Tennessee Bottoms or bottom land. In Memphis, the Tennessee Bottoms end in steep bluffs overlooking the river. To the west of the Tennessee Bottoms is the Mississippi Alluvial Plain, less than 300 feet (90 m) above sea level. This area of lowlands, flood plains, and swamp land is sometimes referred to as the Delta region. Memphis is the economic center of West Tennessee and the largest city in the state.
Most of West Tennessee remained Indian land until the Chickasaw Cession of 1818, when the Chickasaw ceded their land between the Tennessee River and the Mississippi River. The portion of the Chickasaw Cession that lies in Kentucky is known today as the Jackson Purchase.
Climate
Most of the state has a humid subtropical climate, with the exception of some of the higher elevations in the Appalachians, which are classified as having a mountain temperate climate or a humid continental climate due to cooler temperatures. The Gulf of Mexico is the dominant factor in the climate of Tennessee, with winds from the south being responsible for most of the state’s annual precipitation. Generally, the state has hot summers and mild to cool winters with generous precipitation throughout the year, with highest average monthly precipitation generally in the winter and spring months, between December and April. The driest months, on average, are August to October. On average the state receives 50 inches (130 cm) of precipitation annually. Snowfall ranges from 5 inches (13 cm) in West Tennessee to over 16 inches (41 cm) in the higher mountains in East Tennessee.
Summers in the state are generally hot and humid, with most of the state averaging a high of around 90 °F (32 °C) during the summer months. Winters tend to be mild to cool, increasing in coolness at higher elevations. Generally, for areas outside the highest mountains, the average overnight lows are near freezing for most of the state. The highest recorded temperature is 113 °F (45 °C) at Perryville on August 9, 1930 while the lowest recorded temperature is −32 °F (−36 °C) at Mountain City on December 30, 1917.
While the state is far enough from the coast to avoid any direct impact from a hurricane, the location of the state makes it likely to be impacted from the remnants of tropical cyclones which weaken over land and can cause significant rainfall, such as Tropical Storm Chris in 1982 and Hurricane Opal in 1995. The state averages around 50 days of thunderstorms per year, some of which can be severe with large hail and damaging winds. Tornadoes are possible throughout the state, with West and Middle Tennessee the most vulnerable. Occasionally, strong or violent tornadoes occur, such as the devastating April 2011 tornadoes that killed 20 people in North Georgia and Southeast Tennessee. On average, the state has 15 tornadoes per year. Tornadoes in Tennessee can be severe, and Tennessee leads the nation in the percentage of total tornadoes which have fatalities. Winter storms are an occasional problem, such as the infamous Blizzard of 1993, although ice storms are a more likely occurrence. Fog is a persistent problem in parts of the state, especially in East Tennessee.
Major cities
The capital is Nashville, though Knoxville, Kingston, and Murfreesboro have all served as state capitals in the past. Memphis has the largest population of any city in the state. Nashville’s 13-county metropolitan area has been the state’s largest since c. 1990. Chattanooga and Knoxville, both in the eastern part of the state near the Great Smoky Mountains, each has approximately one-third of the population of Memphis or Nashville. The city of Clarksville is a fifth significant population center, some 45 miles (72 km) northwest of Nashville. Murfreesboro is the sixth-largest city in Tennessee, consisting of some 108,755 residents.
|
Rank |
Name |
County |
Pop. |
||
|
Memphis Nashville |
1 |
Memphis |
Shelby |
656,861 |
Knoxville Chattanooga |
|
2 |
Nashville |
Davidson |
644,014 |
||
|
3 |
Knoxville |
Knox |
184,281 |
||
|
4 |
Chattanooga |
Hamilton |
173,778 |
||
|
5 |
Clarksville |
Montgomery |
146,806 |
||
|
6 |
Murfreesboro |
Rutherford |
120,954 |
||
|
7 |
Franklin |
Williamson |
70,612 |
||
|
8 |
Jackson |
Madison |
67,319 |
||
|
9 |
Johnson City |
Washington |
65,813 |
||
|
10 |
Bartlett |
Shelby |
58,264 |
Transportation
Interstate 40 crosses the state in a west-east orientation. Its branch interstate highways include I-240 in Memphis; I-440 in Nashville; I-140 from Knoxville to Alcoa and I-640 in Knoxville. I-26, although technically an east-west interstate, runs from the North Carolina border below Johnson City to its terminus at Kingsport. I-24 is an east-west interstate that runs cross-state from Chattanooga to Clarksville. In a north-south orientation are highways I-55, I-65, I-75, and I-81. Interstate 65 crosses the state through Nashville, while Interstate 75 serves Chattanooga and Knoxville and Interstate 55 serves Memphis. Interstate 81 enters the state at Bristol and terminates at its junction with I-40 near Dandridge. I-155 is a branch highway from I-55. The only spur highway of I-75 in Tennessee is I-275, which is in Knoxville. When completed, I-69 will travel through the western part of the state, from South Fulton to Memphis. A branch interstate, I-269 also exists from Millington to Collierville.
Airports
Major airports within the state include Memphis International Airport (MEM), Nashville International Airport (BNA), McGhee Tyson Airport (TYS) in Alcoa, Chattanooga Metropolitan Airport (CHA), Tri-Cities Regional Airport (TRI), and McKellar-Sipes Regional Airport (MKL), in Jackson. Because Memphis International Airport is the major hub for FedEx Corporation, it is the world’s largest air cargo operation.
Railroads
For passenger rail service, Memphis and Newbern, Tennessee, are served by the Amtrak City of New Orleans line on its run between Chicago, Illinois, and New Orleans, Louisiana. Nashville is served by the Music City Star commuter rail service.
Cargo services in Tennessee are primarily served by CSX Transportation, which has a hump yard in Nashville called Radnor Yard. Norfolk Southern Railway operates lines in East Tennessee, through cities including Knoxville and Chattanooga, and operates a classification yard near Knoxville, the John Sevier Yard. BNSF operates a major intermodal facility in Memphis.