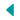
Wisconsin is a U.S. state located in the north-central United States, in the Midwest and Great Lakes regions. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake Michigan to the east, Michigan to the northeast, and Lake Superior to the north. Wisconsin is the 23rd largest state by total area and the20th most populous. The state capital is Madison, and its largest city is Milwaukee, which is located on the western shore of Lake Michigan. The state is divided into 72 counties.
Wisconsin’s geography is diverse, with the Northern Highland and Western Upland along with a part of the Central Plain occupying the western part of the state and lowlands stretching to the shore of Lake Michigan. Wisconsin is second to Michigan in the length of its Great Lakes coastline.
Wisconsin is known as “America’s Dairy land” because it is one of the nation’s leading dairy producers, particularly famous for cheese. Manufacturing, especially paper products, information technology (IT), and tourism are also major contributors to the state’s economy.
Geography
Wisconsin can be divided into five geographic regions.
The Drift less Area of southwestern Wisconsin is characterized by bluffs carved in sedimentary rock by water from melting Ice Age glaciers.
Timms Hill is the highest natural point in Wisconsin at 1951.5 ft. Located in the Town of Hill, Price County.
Wisconsin is bordered by the Montreal River; Lake Superior and Michigan to the north; by Lake Michigan to the east; by Illinois to the south; and by Iowa to the southwest and Minnesota to the northwest. A border dispute with Michigan was settled by two cases, both Wisconsin v. Michigan, in 1934 and 1935. The state’s boundaries include the Mississippi River and St. Croix River in the west, and the Menominee River in the northeast.
With its location between the Great Lakes and the Mississippi River, Wisconsin is home to a wide variety of geographical features. The state is divided into five distinct regions. In the north, the Lake Superior Lowland occupies a belt of land along Lake Superior. Just to the south, the Northern Highland has massive mixed hardwood and coniferous forests including the 1,500,000 acres (6,100 km2) Chequamegon-Nicolet National Forest, as well as thousands of glacial lakes, and the state’s highest point, Timms Hill. In the middle of the state, the Central Plain has some unique sandstone formations like the Dells of the Wisconsin River in addition to rich farmland. The Eastern Ridges and Lowlands region in the southeast is home to many of Wisconsin’s largest cities. The ridges include the Niagara Escarpment that stretches from New York, the Black River Escarpment and the Magnesian Escarpment.
The bedrock of the Niagara Escarpment is dolomite, while the two shorter ridges have limestone bedrock. In the southwest, the Western Upland is a rugged landscape with a mix of forest and farmland, including many bluffs on the Mississippi River. This region is part of the Driftless Area, which also includes portions of Iowa, Illinois, and Minnesota. This area was not covered by glaciers during the most recent ice age, the Wisconsin Glaciation. Overall, 46% of Wisconsin’s land area is covered by forest. Langlade County has a soil rarely found outside of the county called Antigo Silt Loam.]
Wisconsin has sister-state relationships with the Germany’s Hesse, Japan’s Chiba Prefecture, Mexico’s Jalisco, China’s Heilongjiang, and Nicaragua.
The pole of inaccessibility for Wisconsin, located approximately 15 miles (24 km) southwest of Wausau at44.8824°N 89.912°W, marks the location furthest from any point not within Wisconsin.
Climate
The southern third of Wisconsin is classified as hot summer humid continental climate (Köppen Dfa) and the colder northern portion is classified as warm summer humid continental climate (Köppen Dfb). The highest temperature ever recorded in the state was in the Wisconsin Dells, on July 13, 1936, where it reached 114 °F (46 °C). The lowest temperature ever recorded in Wisconsin was in the village of Couderay, where it reached −55 °F (−48 °C) on both February 2 and 4, 1996. Wisconsin also receives a large amount of regular snowfall averaging around 40 inches in the southern portions with up to 160 inches annually in the Lake Superior Snow Belt each year.
Transportation
Wisconsin is served by eight commercial service airports, in addition to a number of general aviation airports.
The Wisconsin Department of Transportation is responsible for planning, building and maintaining the state’s highways. Seven Interstate Highways transverse the state.
Amtrak provides daily passenger rail service between Chicago and Milwaukee. It also provides cross-country service via the Empire Builder with station stops in several cities in Wisconsin.
Important Municipalities
Over 68% of Wisconsin residents live in urban areas, with the Greater Milwaukee area home to roughly one-third of the state’s population. Milwaukee is at the northern edge of an urban area bordering Lake Michigan that stretches southward into greater Chicago and northwestern Indiana, with a population of over 11 million. With over 594,000 residents, Milwaukee is the 30th-largest city in the country. The string of cities along the western edge of Lake Michigan is generally considered to be an example of a megalopolis.
With a population of around 233,000 and metropolitan area of over 600,000, Madison has a dual identity as state capital and college town. Madison’s suburb, Middleton, was ranked the “Best Place to Live in America” in 2007 by Money Magazine. Medium-size cities dot the state and anchor a network of working farms surrounding them. As of 2011, there were 12 cities in Wisconsin with a population of 50,000 or more, accounting for 73% of the state’s employment.
Wisconsin has three types of municipality: cities, villages, and towns. Cities and villages are incorporated urban areas. Towns are unincorporated minor civil divisions of counties with limited self-government.
|
Rank |
Name |
County |
Pop. |
||
|
Milwaukee Madison |
1 |
Milwaukee |
Milwaukee |
598,916 |
Green Bay Kenosha |
|
2 |
Madison |
Dane |
240,323 |
||
|
3 |
Green Bay |
Brown |
104,868 |
||
|
4 |
Kenosha |
Kenosha |
100,150 |
||
|
5 |
Racine |
Racine |
78,303 |
||
|
6 |
Appleton |
Outagamie |
73,016 |
||
|
7 |
Waukesha |
Waukesha |
70,920 |
||
|
8 |
Oshkosh |
Winnebago |
66,653 |
||
|
9 |
Eau Claire |
Eau Claire |
66,966 |
||
|
10 |
Janesville |
Rock |